|
#2
January 30th, 2018, 12:51 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Central Board Of Secondary Education Syllabus
I am providing you the syllabus of Economics of Class XI of Central Board Of Secondary Education CBSE CBSE Class XI Economics syllabus Theory: 80 Marks Units Part A Statistics for Economics 1. Introduction 2. Collection, Organisation and Presentation of Data 3. Statistical Tools and Interpretation Part B Indian Economic Development 4. Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991 5. Current Challenges facing Indian Economy 6. Development Experience of India - A Comparison with Neighbours Theory Paper (40+40 = 80 Marks) Part C Project Work Part A: Statistics for Economics In this course, the learners are expected to acquire skills in collection, organisation and presentation of quantitative and qualitative information pertaining to various simple economic aspects systematically. It also intends to provide some basic statistical tools to analyse, and interpret any economic information and draw appropriate inferences. In this process, the learners are also expected to understand the behaviour of various economic data. Unit 1: Introduction 07 Periods What is Economics? Meaning, scope, functions and importance of statistics in Economics Unit 2: Collection, Organisation and Presentation of data 27 Periods Collection of data - sources of data - primary and secondary; how basic data is collected, with concepts of Sampling; Sampling and Non-Sampling errors; methods of collecting data; some important sources of secondary data: Census of India and National Sample Survey Organisation. Organisation of Data: Meaning and types of variables; Frequency Distribution. Presentation of Data: Tabular Presentation and Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: (i) Geometric forms (bar diagrams and pie diagrams), (ii) Frequency diagrams (histogram, polygon and ogive) and (iii) Arithmetic line graphs (time series graph) Unit 3: Statistical Tools and Interpretation 66 Periods (For all the numerical problems and solutions, the appropriate economic interpretation may be attempted. This means, the students need to solve the problems and provide interpretation for the results derived.) Measures of Central Tendency- mean (simple and weighted), median and mode Measures of Dispersion - absolute dispersion (range, quartile deviation, mean deviation and standard deviation); relative dispersion (co-efficient of range, co-efficient of quartile-deviation, co-efficient of mean deviation, co-efficient of variation); Lorenz Curve: Meaning, construction and its application. Correlation – meaning and properties, scatter diagram; Measures of correlation - Karl Pearson's method (two variables ungrouped data) Spearman's rank correlation. Introduction to Index Numbers - meaning, types - wholesale price index, consumer price index and index of industrial production, uses of index numbers; Inflation and index numbers. Part B: Indian Economic Development Unit 4: Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991: 28 Periods A brief introduction of the state of Indian economy on the eve of independence. Common goals of Five Year Plans. Main features, problems and policies of agriculture (institutional aspects and new agricultural strategy, etc.), industry (industrial licensing, etc.) and foreign trade. Economic Reforms since 1991: Need and main features - liberalisation, globalisation and privatisation; An appraisal of LPG policies Unit 5: Current challenges facing Indian Economy 60 Periods Poverty- absolute and relative; Main programmes for poverty alleviation: A critical assessment; Rural development: Key issues - credit and marketing - role of cooperatives; agricultural diversification; alternative farming - organic farming Human Capital Formation: How people become resource; Role of human capital in economic development; Growth of Education Sector in India Employment: Formal and informal, growth and other issues: Problems and policies. Infrastructure: Meaning and Types: Case Studies: Energy and Health: Problems and Policies- A critical assessment; Sustainable Economic Development: Meaning, Effects of Economic Development on Resources and Environment, including global warming. Unit 6: Development Experience of India: 12 Periods A comparison with neighbours India and Pakistan India and China Issues: growth, population, sectoral development and other developmental indicators For complete syllabus here is the attachment CBSE Class XI Economics syllabus  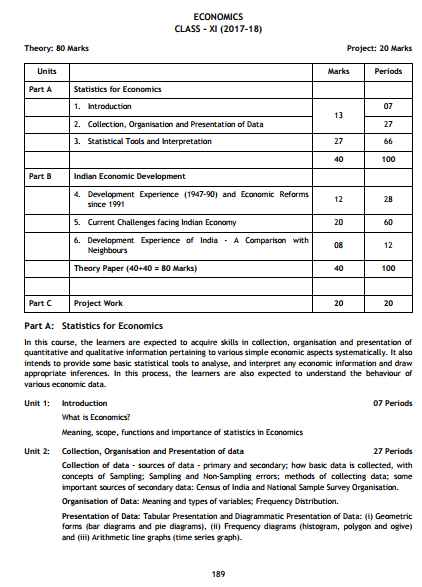 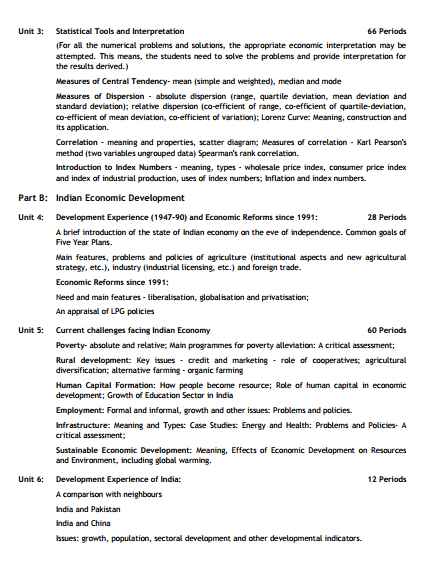 |