|
#2
June 15th, 2016, 03:36 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Dy Patil AICET Syllabus
Dr. D.Y.Patil conducts All India Common Entrance Test for admission to undergraduate courses in of Bachelor in Medicine and Surgery (MBBS) and Bachelor in Dental Surgery (BDS). The total duration of the exam is 3 hours and there will be a total of 200 multiple choice type questions. 50 questions for Physics, Chemistry, Botany and Zoology each,, Dr. D.Y.Patil All India Common Entrance Test syllabus  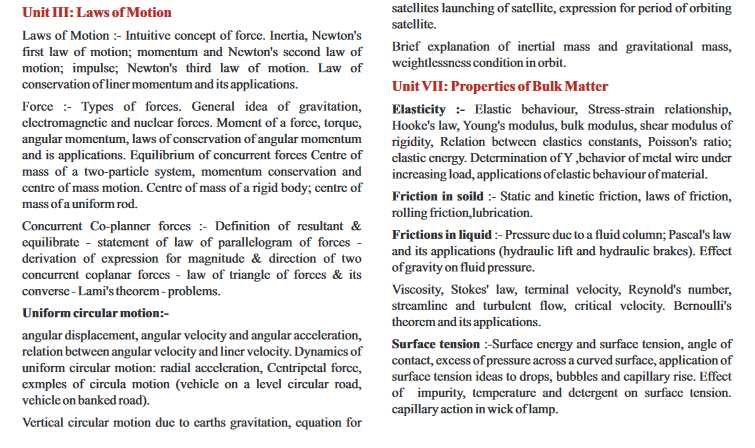    Dr D.Y Patil Institute AICET Biology Syllabus: Unit I Diversity of Living Organism : Introduction to Biology : Defination of Biology and its main branches, Botany and Zoology, scope of Biology, branches of Biology ( defmition ).Classical branches – morphology, cytology, histology, anatomy, physiology, developmental Biology, biosystematics, genetics, ecology, organic evolution and palaeontology. Inter disciplinary branches – biophysics, biochemistry, and biostatistics. Applied branches and career prospects – agriculture, entomology, sylviculture, pathology, apiculture, microbiology, and bioinformetics. Role of Biology in myths and disbeliefs. Biosystematics : What is life? biodiversity; need for classification; Three domains of life, concept of species:- three domains of life; taxonomy & systematics; concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; binomial nomenclature; tools for study of taxonomy- museums, zorogical parks, herbaria, botanical gardens. Five kingdom classification; salient features and classification of Monera, Protista and Fungi ( mycota ) into major groups: Lichens. Viruses and Viroid, prions : Chemical nature with one example of disease each-creutzfeldt – Jacob disease ( CZD ) and potato spindle tuber disease ( PSTD ) Kingdom Plantae : Salient features and classification of plants into major groups – Algae, Bryophyta ( metaphyta ), Pteridophyta, Gymnospermae and Angiospermae ( three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category ); Angiosperms – classification up to class, characteristic features and examples. Kingdom – Animalia : Salient features and classification of animals non chordates up to phyla level and chordates up to classes level ( three to five salient features and at least two examples ). Unit II Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants : Morphology of Plants : Morphology and modifications; tissues; anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: root, stem, leaf, inflorescence; cymose and racemose, flower ( homochlamydeous, heterochlamydeous ) fruit and seed ( to be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical Syllabus ). Study of Animal tissues : Animal tissues ( epithelial, connective, nervous, muscular ) Study of Animal Type Example Cockroach : morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems ( digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive ) of an insect ( cockroach ), ( a brief account only ) Unit III Cell Biology : Organisation of cell : Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles – structure and function; endomembrane system, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, microbodies; cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles ( ultrastructure and function ); nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus. Biochemistry of cell : Chemical constituents of living cells: biomolecules, structure and function of proteins, carbodydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, enzymes, types, properties, enzyme action. Cell Reproduction : cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance. Unit IV : Plant Physiology Plant water relation & mineral nutrition : Transport in plants; movement of water, gases and nutrients; cell to cell transport, Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport; plant-water relations, Imbibition, water potential, osmosis, plasmolysis; long distance transport of water – Absorption, apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and guttation; transpiration, opening and closing of stomata; Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients – Transport of food, phloem transport, mass flow hypothesis; diffusion of gases. Mineral nutrition: Essential minerals, macro and micronutrients and their role; deficiency symptoms; mineral toxicity; elementary idea of hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition; nitrogen metabolism, nitrogen cycle, biological nitrogen fixation. Photosynthesis : Bioenergetics – introduction, light as the source of energy and ATP as energy currency, photosynthesis as a means of autotrophic nutrition; site of photosynthesis – chloroplst pigments involved in photosynthesis ( elementary idea ); photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation; chemiosmotic hypothesis; photorespiration; C3 and C4 pathways; factors affecting photosynthesis. Respiration : Exchange of gases; cellular respiration – glycolysis, fermentation ( anaerobic ), TCA cycle and electron transport system ( aerobic ); energy relations – number of ATP molecules generated; amphibolic pathways; respiratroy quotient, Pasteur effect. Plant growth and development: seed germination; phases of plant growth and plant growth rate; conditions of growth; differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; sequence of developmental processes in a plant cell; growth regulators – auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA; seed dormancy; vernalisation; photoperiodism. Here I’m attaching PDF of Dr. D.Y.Patil All India Common Entrance Test syllabus: |