|
#2
October 23rd, 2017, 08:55 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Economics General Syllabus of Calcutta University
Here I am providing complete syllabus of BA (Honours and General): Economics Course of Calcutta University: Calcutta University BA (Honours and General): Economics Course Syllabus Year I Paper IA Microeconomic Principles Paper IB Macroeconomic Principles Paper IIA Statistics for Economics Paper IIB Mathematics for Economics Year II Paper IIIA Microeconomics Paper IIIB Macroeconomics Paper IVA Development Theory Paper IVB Indian Economy Since Independence Year III Paper VA International Economics Paper VB Public Economics Paper VIA Comparative Development Experience Paper VIB Contemporary Economic Issues: India and West Bengal Paper VIIA Statistics & Basic Econometrics Paper VIIB Applied Economics PaperVIIIA Indian Economic History PaperVIIIB Term Paper The Economic Way of Thinking 18 1.1 Normative Economics and Positive Economics - Methodology 1.2 Wants, Scarcity, Competing Ends and Choice - Defining Economics 1.3 Basic Economic Questions, Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. Lipsey, Chapter 1 and Chapter 4. Mankiw, chapter 2. 1.4 Principles of Microeconomics – principles of individual decision making and principles of economic interactions – Introduce trade Off, Opportunity Cost, Efficiency, Marginal Changes and Cost-Benefit, Trade, Market economy, Market failure, Externality and Market power. Mankiw, Chapter 1, Stockman Chapter 1 1.5 Interdependence and the Gains from Trade – production possibilities frontier and increasing costs, absolute and comparative advantage, comparative advantage and gains from trade. Mankiw, Chapter 3, Stockman Chapter 2. Market and Adjustments 25 2.1 The Evolution of Market Economies. Price System and the Invisible Hand. Lipsey Chapter 5, (page 59-61). 2.2 The Decision-takers – households, firms and central authorities 2.3 The Concepts of Markets – individual market, separation of individual markets, interlinking of individual markets. Difference among markets – competitiveness, goods and factor markets, free and controlled markets. Market and non-market sectors, public and private sectors, economies – free market, command and mixed. 2.4 Different Goods: Public goods, Private goods, Common resources and Natural Monopolies Lipsey Chapter 6, 67-71, Mankiw Chapter 11 (201-203), Lipsey and Chrystal Chapter 13 (278). 2.5 Market and competition; Demand and its determinants; Supply and its determinants; relation of Quantity Demand with Price (using arguments of income and substitution effects); relation of Quantity Supply with Price (using increasing costs argument); Laws of Demand and Supply; Demand and Supply as Planning Curves; movement along and shift of the curve; Demand, Supply and Other factors. 2.6 Equilibrium and Disequilibrium 2.7 Market Adjustment without Government (with illustrations) Mankiw, Chapter 4. Lipsey and Chrystal, Chapter 3. Stockman Chapter Market Sensitivity and Elasticity 3.1 Importance of Elasticity in Choice-Decisions 3.2 Method of Calculation – Arc Elasticity. Point Elasticity – definition. 3.3 Demand and Supply Elasticities – types of elasticity and factors effecting elasticity. 3.4 Demand Elasticity and Revenue 3.5 Income and Cross Price elasticity 3.6 Long run and Short Run elasticities of Demand and Supply 3.7 Case Studies – OPEC and Oil Price, Illegal Drugs Mankiw, Chapter 5. Stockman, Chapter 5. Lipsey and Chrystal, Chapter 4 Calcutta University BA (Honours and General): Economics Course Syllabus 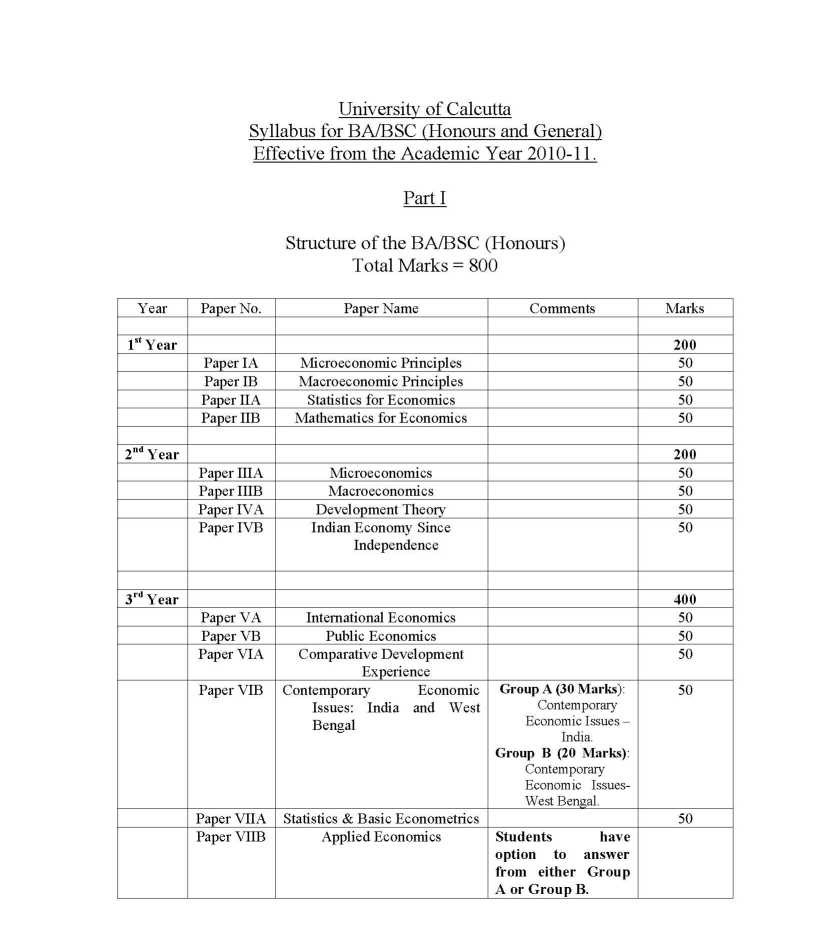  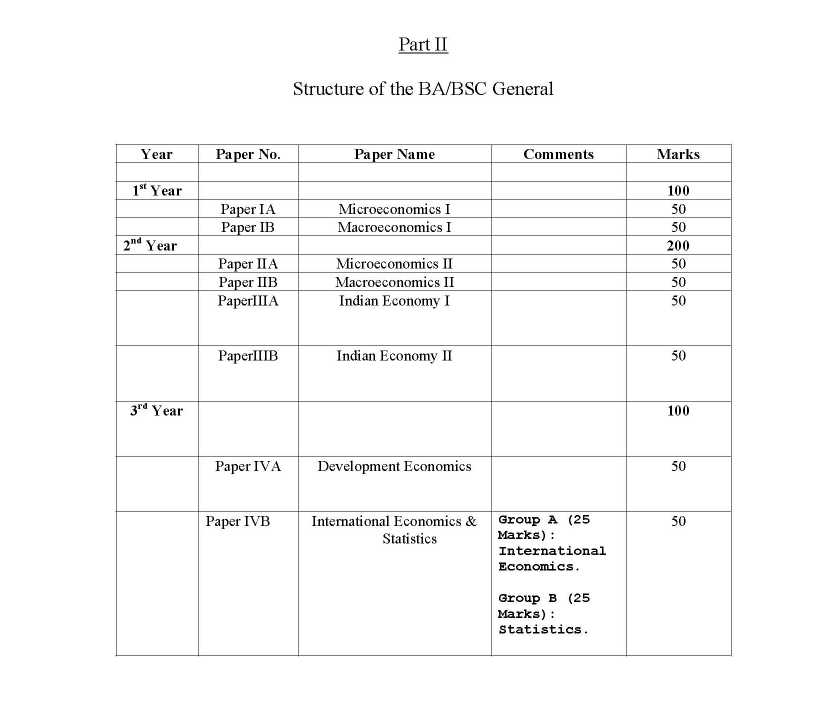 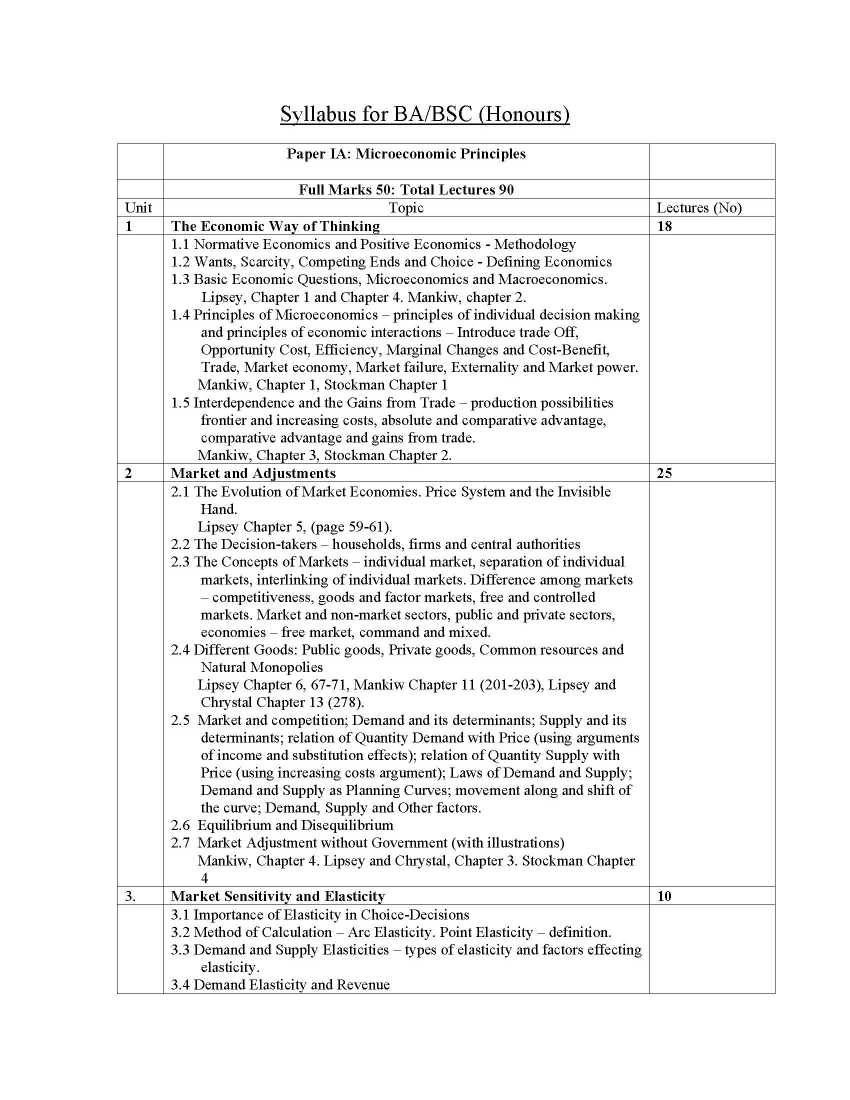 |