The Karnataka Secondary Education Examination Board, better and abbreviated as, KSEEB came into existence in the year 1964, has been conducting SSLC and other examinations.
Please find the below attached file for the Previous year SSLC Mathematics Kannada Medium question papers:
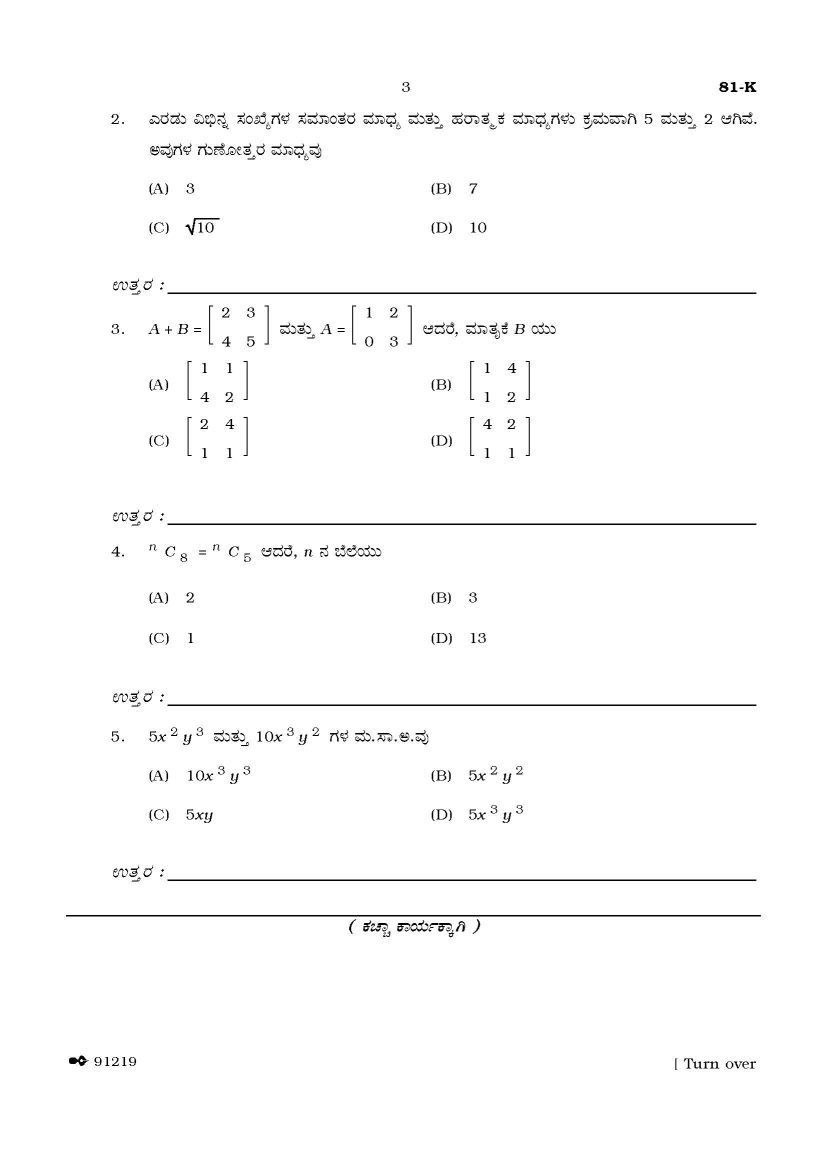
SSLC Mathematics Kannada Medium question paper1


 Karnataka Board SSLC Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus – Part 1
Karnataka Board SSLC Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus – Part 1
Arithmetic Progressions
Arithmetic Progression Derivation of the nth term and sum of the first n terms of A.P. and their application in solving daily life problems.
Triangles
Definitions, examples, counter examples of similar triangles.
(Prove) If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
(Motivate) If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side.
(Motivate) If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are equal, their corresponding sides are proportional and the triangles are similar.
(Motivate) If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, their corresponding
angles are equal and the two triangles are similar.
(Motivate) If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional, the two triangles are similar.
(Motivate) If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse, the triangles on each side of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other.
(Prove) The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of their corresponding sides.
(Prove) In a right triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
(Prove) In a triangle, if the square on one side is equal to sum of the squares on the other two sides, the angles opposite to the first side is a right angle.
Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Pair of linear equations in two variables and graphical method of their
solution, consistency/inconsistency.
Algebraic conditions for number of solutions. Solution of a pair of linear equations in two
variables algebraically – by substitution, by elimination and by cross multiplication
method. Simple situational problems. Simple problems on equations reducible to linear
equations.
Circles
Tangent to a circle at, point of contact
(Prove) The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
(Prove) The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
Areas Related to Circles
Motivate the area of a circle; area of sectors and segments of a circle. Problems based on
areas and perimeter / circumference of the above said plane figures. (In calculating area
of segment of a circle, problems should be restricted to central angle of 60°, 90° and 120°
only. Plane figures involving triangles, simple quadrilaterals and circle should be taken.)
Constructions
Division of a line segment in a given ratio (internally).
Tangents to a circle from a point outside it.
Construction of a triangle similar to a given triangle.
Coordinate Geometry
Review: Concepts of coordinate geometry, graphs of linear equations. Distance formula.
Section formula (internal division). Area of a triangle.
Real Numbers
Euclid’s division lemma, Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic – statements after reviewing
work done earlier and after illustrating and motivating through examples, Proofs of
irrationality of √2, √3, √5 Decimal representation of rational numbers in terms of
terminating/non-terminating recurring decimals.
Karnataka Board SSLC Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus – Part 2
Polynomials
Zeros of a polynomial. Relationship between zeros and coefficients of quadratic
polynomials. Statement and simple problems on division algorithm for polynomials with
real coefficients.
Quadratic Equations
Standard form of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, (a ≠ 0). Solutions of quadratic
equations (only real roots) by factorization, by completing the square and by using quadratic
formula. Relationship between discriminant and nature of roots.
Situational problems based on quadratic equations related to day to day activities to be
incorporated.
Introduction To Trigonometry
Trigonometric ratios of an acute angle of a right-angled triangle. Proof of their existence
(well defined); motivate the ratios whichever are defined at 0 and 90. Values (with proofs) of the trigonometric ratios of 30°, 45° and 60°. Relationships between the ratios.
Some Applications Of Trigonometry
Proof and applications of the identity sin2A + cos2A = 1. Only simple identities to be given.Trigonometric ratios of complementary angles.
Statistics
Mean, median and mode of grouped data (bimodal situation to be avoided).Cumulative frequency graph.
Probability
Classical definition of probability. Simple problems on single events (not using set
notation).
Surface Areas And Volumes
Surface areas and volumes of combinations of any two of the following: cubes, cuboids,
spheres, hemispheres and right circular cylinders/cones. Frustum of a cone.
Problems involving converting one type of metallic solid into another and other mixed problems. Problems with combination of not more than two different solids be taken).
Proofs In Mathematics
Mathematical Modelling