|
#2
October 4th, 2017, 12:19 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: ln Base E
The common logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the scientific consistent e, where e is a nonsensical and supernatural number around equivalent to 2.718281828459. The normal logarithm of x is for the most part composed as ln x, loge x, or once in a while, if the base e is certain, essentially log x. Brackets are now and then included for clearness, giving ln(x), loge(x) or log(x). This is done specifically when the contention to the logarithm is not a solitary image, to forestall equivocalness. Why e is the base of regular logarithm work? The consistent can be described in various ways. For instance, e can be characterized as the novel positive number a with the end goal that the diagram of the capacity y = hatchet has unit incline at x = 0. ... The normal logarithm, or logarithm to base e, is the converse capacity to the common exponential capacity. The characteristic logarithm of x is the ability to which e would need to be raised to break even with x. For instance, ln(7.5) is 2.0149..., in light of the fact that e2.0149... = 7.5. The normal log of e itself, ln(e), is 1, in light of the fact that e1 = e, while the characteristic logarithm of 1, ln(1), is 0, since e0 = 1. The meaning of the normal logarithm can be reached out to give logarithm esteems for negative numbers and for all non-zero complex numbers, in spite of the fact that this prompts a multi-esteemed capacity: see Complex logarithm. The natural logarithm function, if measured as a real-valued function of a real variable, is the inverse function of the exponential function, leading to the similarities: 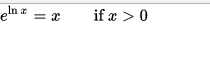 Like all logarithms, the natural logarithm maps multiplication into accumulation: 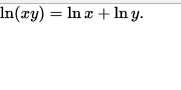 Thus, the logarithm function is a group isomorphism from positive real numbers under multiplication to the group of real numbers under addition, represented as a function:  |