|
#2
September 23rd, 2016, 08:24 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Syllabus for HPCL Recruitment
As per your request here I am giving you syllabus for Mechanical Engineering stream students for Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) recruitment for Engineer trainee. Mechanical Engineering – Syllabus 1 Engineering Mechanics Free body diagrams and equilibrium; trusses and frames; virtual work; kinematics and dynamics of particles and of rigid bodies in plane motion, including impulse and momentum (linear and angular) and energy formulations; impact. 2 Engineering Materials Structure and properties of engineering materials and their applications, heat treatment, stress-strain diagrams for engineering materials. 3 Strength of Materials Stress and strain, stress-strain relationship and elastic constants, Mohr’s circle for plane stress and plane strain, thin cylinders, thickwalled vessels; shear force and bending moment diagrams; bending and shear stresses; deflection of beams; torsion of circular members; columns and struts; strain energy and impact loading; thermal stresses; Rotating Rims & Discs; Bending of Curved Bars. 4 Theory of Machines Displacement, velocity and acceleration analysis of plane mechanisms, kinematic synthesis of mechanisms; dynamic analysis of slidercrank mechanism; gear trains; flywheels; static and dynamic force analysis; balancing of rotating components; governors. 5 Thermodynamics Thermodynamic system and processes; Zeroth, First and Second laws of thermodynamics;; Carnot cycle. irreversibility and availability; behaviour of pure substances, ideal and real gases; calculation of work and heat in ideal and real processes; Rankine and Brayton cycles with modifications, analysis of thermodynamic cycles related to energy conversion; vapour refrigeration cycle, heat pumps, gas refrigeration, reverse Brayton cycle; moist air: psychrometric chart, basic psychrometric processes. 6 Energy Conversion Fuels and combustion; high pressure steam boilers; flow through nozzles; Gas turbines with intercooling, reheat and regenerators, Steam turbines, velocity diagram, power output and efficiency, maximum blade efficiency of single stage impulse turbine, blade friction, compounding of impulse turbine; reaction turbine, degree of reaction, velocity diagram, power output, efficiency; losses in steam turbines, stage efficiency, overall efficiency and reheat factor; governing of steam turbines; steam condensers, condenser vacuum, sources of air leakage & its disadvantages. 7 Heat-Transfer: Modes of heat transfer; one dimensional heat conduction, resistance concept, electrical analogy, unsteady heat conduction, fins; dimensionless parameters in free and forced convective heat transfer, various correlations for heat transfer in flow over flat plates and through pipes; thermal boundary layer; effect of turbulence; radiative heat transfer, black and grey surfaces, shape factors, network analysis; heat exchanger performance, LMTD and NTU methods. 8 Fluid Mechanics Fluid properties; fluid statics, manometry, buoyancy; control-volume analysis of mass, momentum and energy; fluid acceleration; differential equations of continuity and momentum; Bernoulli’s equation; viscous flow of incompressible fluids; boundary layer; elementary turbulent flow; flow through pipes, head losses in pipes, bends etc. 9 Vibrations Free and forced vibration of single degree of freedom systems; effect of damping; harmonically excited and transient vibrations; introduction to multi-degree of freedom systems; vibration isolation; resonance, critical speeds of shafts. 10 Design Design for static and dynamic loading; failure theories; fatigue strength and the S-N diagram; principles of the design of machine elements such as bolted, riveted and welded joints, shafts, spur gears, rolling and sliding contact bearings, keys, couplings, brakes and clutches; Selection of Materials. Engineer Trainee Mechanical Engineering Syllabus 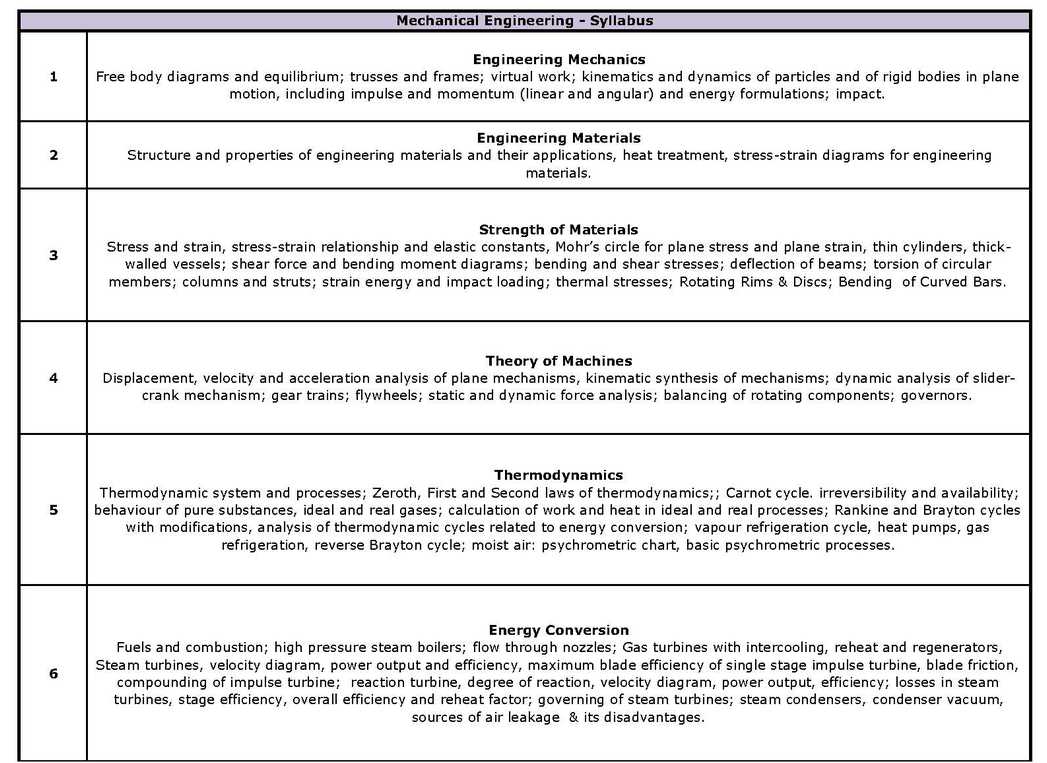 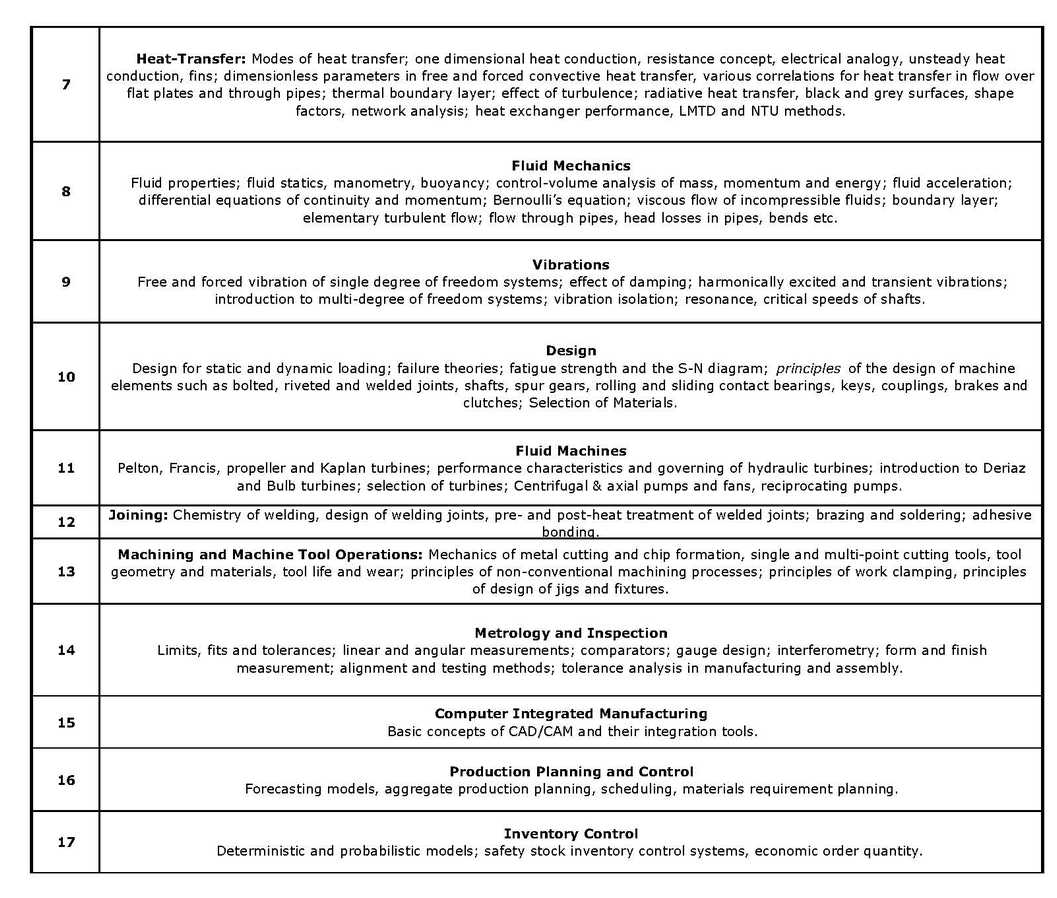 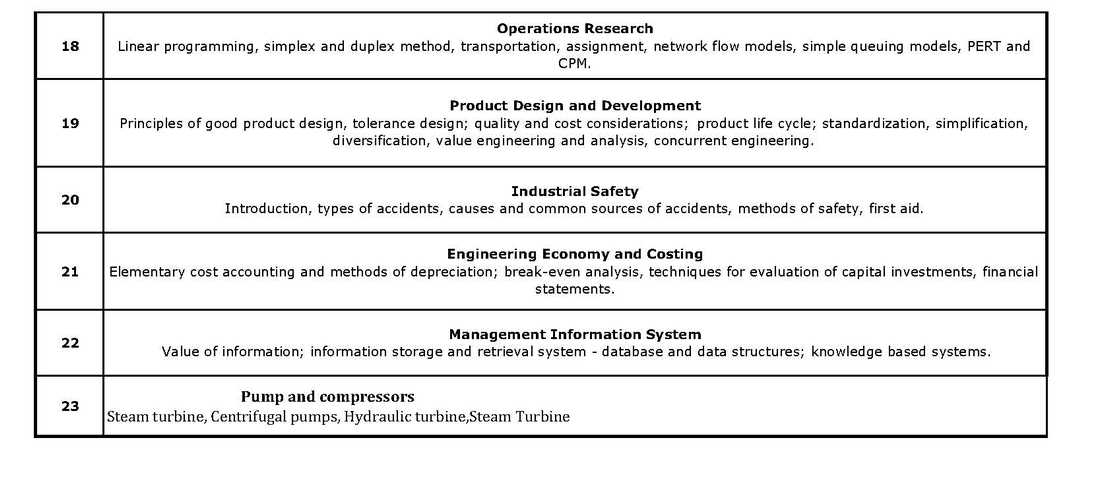 |