|
#2
June 6th, 2016, 04:39 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Brief History of ISRO
Indian Space Research Organisation was founded in 1969 to develop an independent Indian space program. Its headquarters are in Bangalore (Bengaluru). Its chief executive is a chairman, who is also chairman of the Indian government’s Space Commission and the secretary of the Department of Space. ISRO operates through a countrywide network of centres. Sensors and payloads are developed at the Space Applications Centre in Ahmedabad. Satellites are designed, developed, assembled, and tested at the ISRO Satellite Centre in Bangalore. Launch vehicles are developed at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre in Thiruvananthapuram. Launches take place at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre on Sriharikota Island, near Chennai. The Master Control Facilities for geostationary satellite station keeping are located at Hassan and Bhopal. ISRO’s first satellite, Aryabhata, was launched by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1975. Rohini, the first satellite to be placed in orbit by an Indian-made launch vehicle (the Satellite Launch Vehicle 3), was launched on July 18, 1980. ISRO has launched several space systems, including the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system for telecommunication, television broadcasting, meteorology, and disaster warning and the Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites for resource monitoring and management. The first INSAT was launched in 1988, and the program expanded to include geosynchronous satellites called GSAT. The first IRS satellite was also launched in 1988, and the program developed more-specialized satellites, including the Radar Imaging Satellite-1 (RISAT-1, launched in 2012) and the Satellite with Argos and Altika (SARAL, launched in 2013), a joint Indian-French mission that measures ocean wave heights. ISRO subsequently developed three other rockets: the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) for putting satellites into polar orbit, the Geostationary Space Launch Vehicle (GSLV) for placing satellites into geostationary orbit, and a heavy-lift version of the GSLV called the GSLV Mark III or LVM Organisation Structure 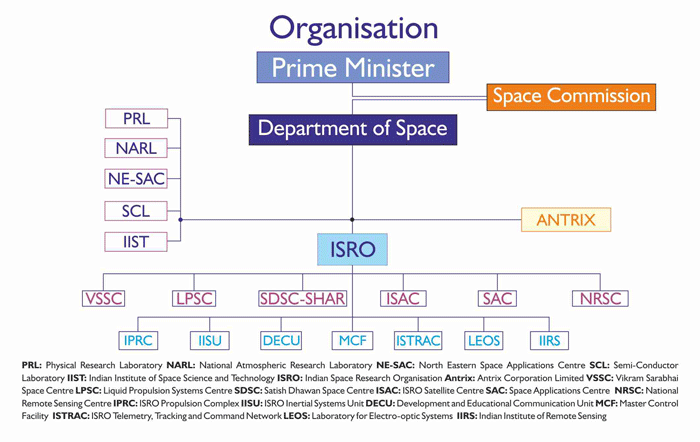 ISRO Centres -Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) -Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) -SDSC SHAR -ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC) -IPRC Mahendragiri -Space Applications Centre (SAC) -National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) -ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) -ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) -Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems (LEOS) -Development and Educational Communication Unit (DECU) -Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST) -Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS) -Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) -National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL) -Master Control Facility (MCF) -North Eastern-Space Applications Centre (NE-SAC) -Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL) -Department of Space and ISRO HQ -Antrix Corporation Limited |